The Urinary Bladder
Definition
Urinary bladder is an organ which stores urine.
Situation
In the pelvic cavity - when distended with urine rises into the abdominal cavity.
Relations
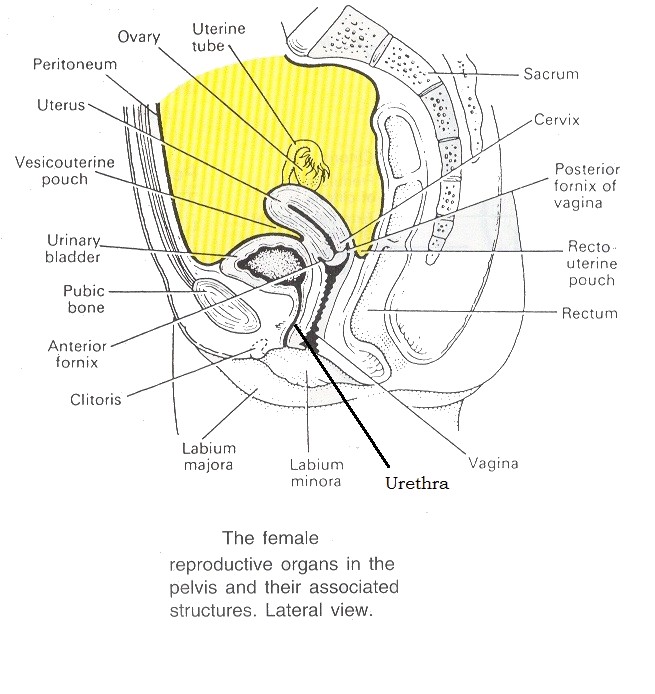
In the female
- anteriorly the symphysis pubis
- posterorly the uterus and upper part of the vagina
- superiorly the small intestine
- inferiorly the urethra and the muscles forming the pelvic floor
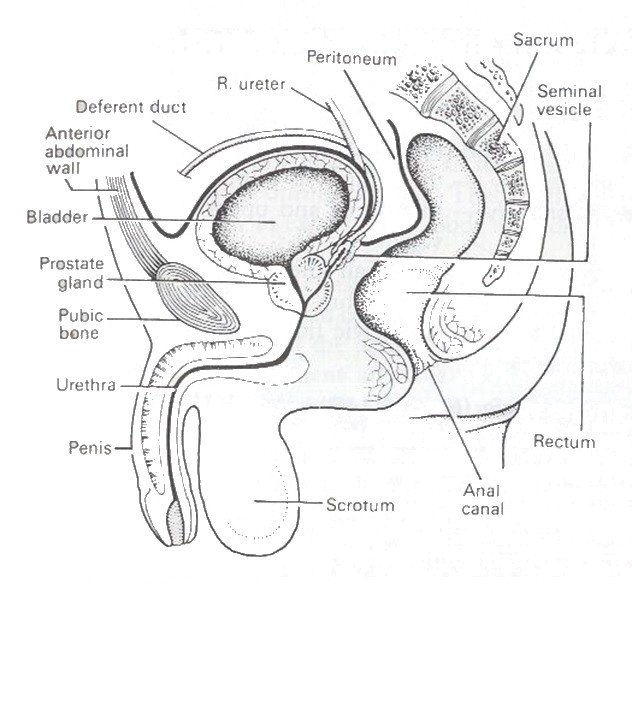
In the male
- anteriorly the symphysis pubis
- posteriorly the rectum and seminal vesicles
- superiorly the small intestine
- inferiorly the urethra and prostate gland.
Structure
Pear shaped
Oval when filled with urine
Anterior superior and posterior surfaces
Posterior surface is called the base
Opens into the urethra at the neck, the lowest point.
Peritoneum covers only the superior surface
From superior surface the peritoneum goes to the anterior abdominal wall - parietal peritoneum.
Posteriorly the peritoneum is reflected on to the uterus in the female and to the rectum in the male.
Bladder wall
Three layers
- outer layer - loose connective tissue - vessels, lymphatics, nerves - on the superior surface- peritoeum.
- Middle layer - smooth muscle fibres, elastic tissue - detrusor muscle - contracts to empty the bladder
- Iinner layer of transitional epithelium
The inner
When empty the inner lining folds - rugae
300 to 400 ml - desire to pass urine (desire to void)
maximum 600 ml
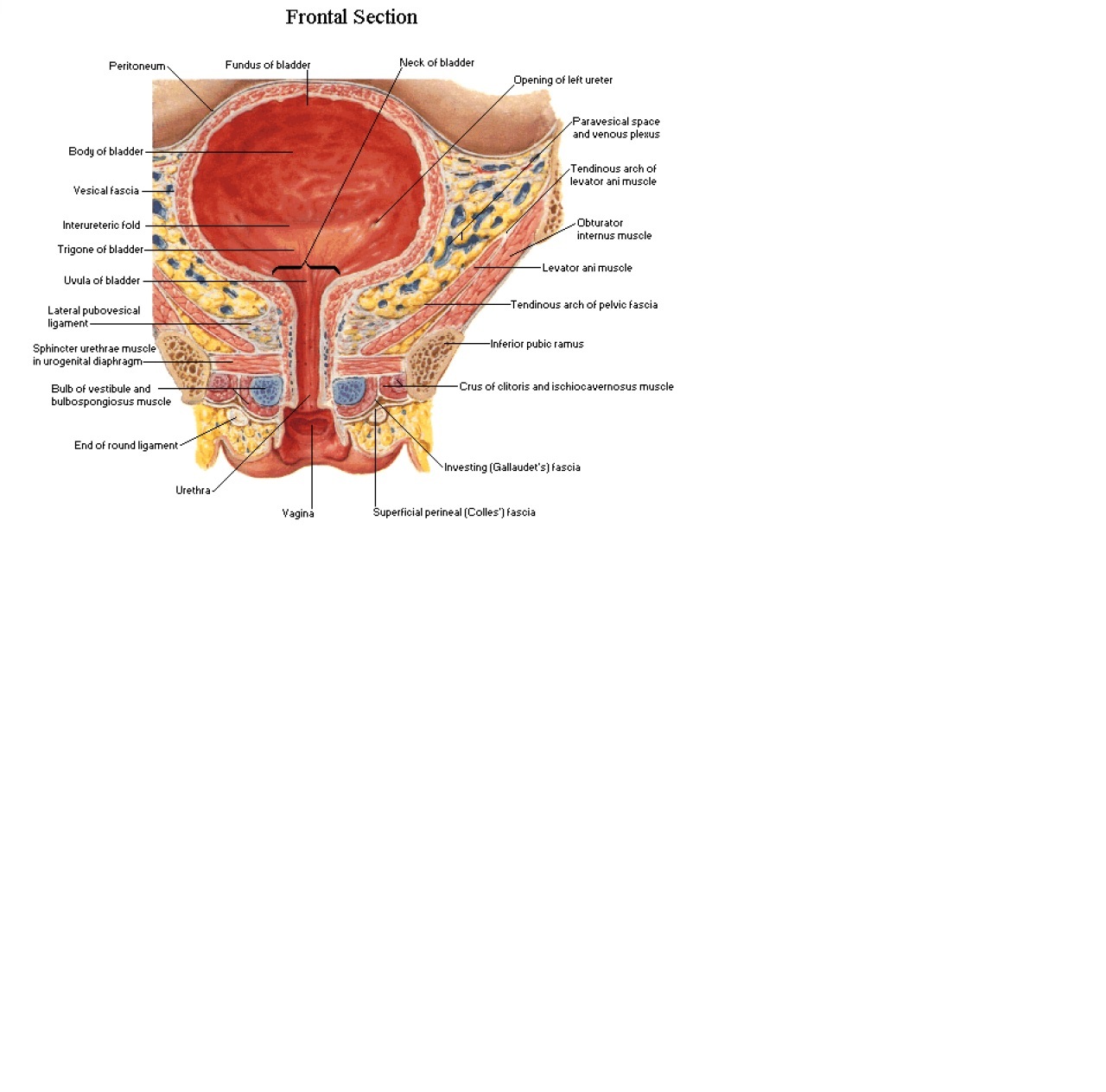
at the base there is trigone
trigone consists of two ureteric openings and the internal urethral opening.
The internal sphincter controls flow of urine from bladder into the urethra
The sphincter is under the control of the autonomic nervous control.
Applied anatomy
Mild obstruction - increased effort to empty - hypertrophy of bladder muscle
Spinal injuries - abnormalities in emptying the bladder - neurogenic bladder
Functions of urinary bladder
Reservoir ( storage ) for urine
In infants:-
When full, spinal reflex action is initiated by stretching of the bladder
Bladder emptied by impulses through autonomic efferent fibres
At that time the internal urethral sphincter relaxes
In adults:-
Micturition (passing urine) reflex is stimulated and the impulses pass to the brain
It creates a desire to pass urine
The reflex contraction of the bladder and internal sphincter is controlled by conscious effort for some time.
In adults micturition occurs by contraction of the detrusor muscle - reflex relaxation of internal sphincter and voluntary relaxation of the external sphincter. Assisted by lowering of diaphragm, contraction of abdominal muscles - Valsalva's manoeuvre
Bladder is obstructed by enlargement of prostate gland in old age, by stricture of urethra after gonorrohea.